Hobbies & Leisure
Trending Paper Craft Ideas for 2025

Hobbies & Leisure
Merging Paper Crafts with Digital Designs
Featured

Hobbies & Leisure
How To Organize Your Paper Crafting Supplies
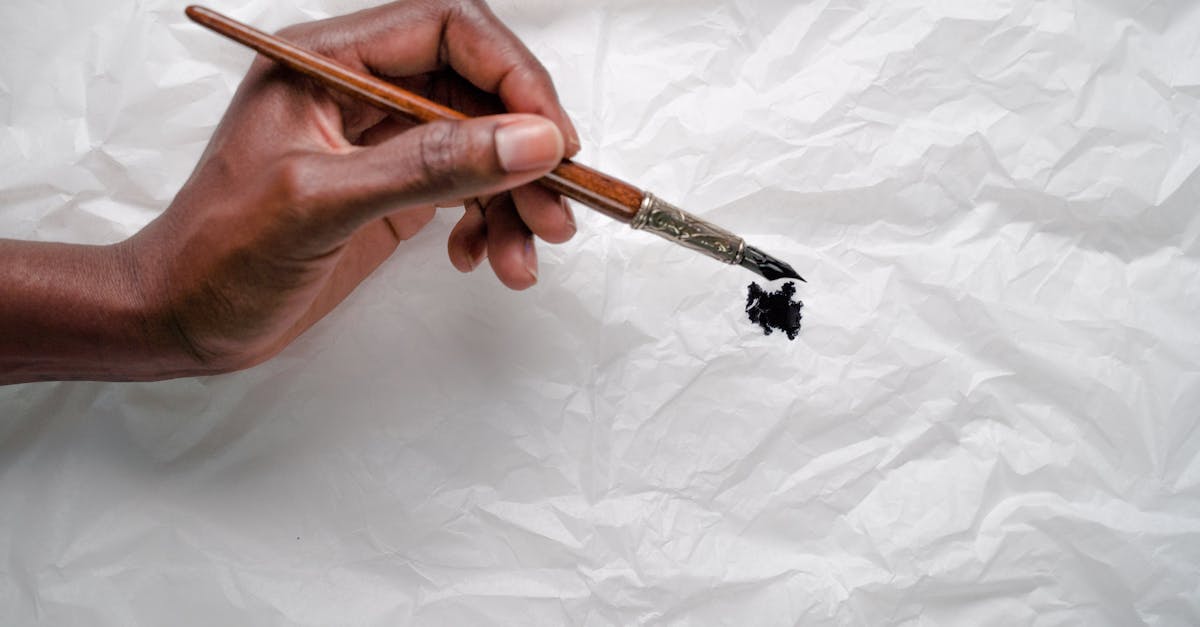

Hobbies & Leisure
Paper Quilling Art Techniques and Fun Projects
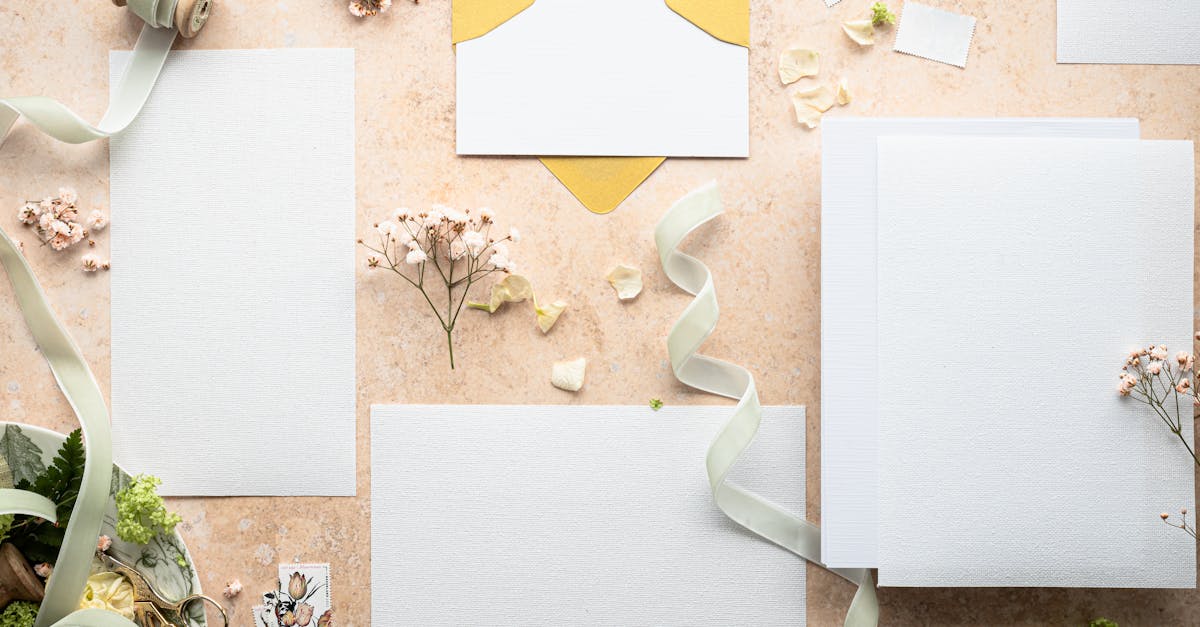

Hobbies & Leisure
DIY Wedding Decor with Paper Crafts
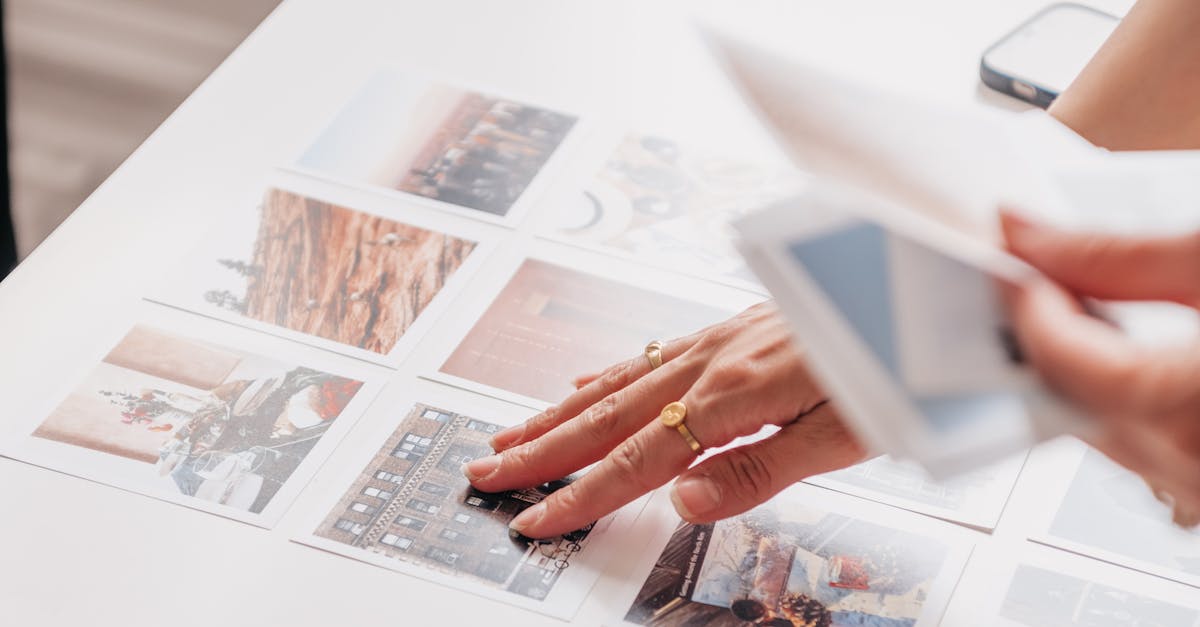

Hobbies & Leisure
Scrapbook Layout Ideas Preserve Memories Creatively
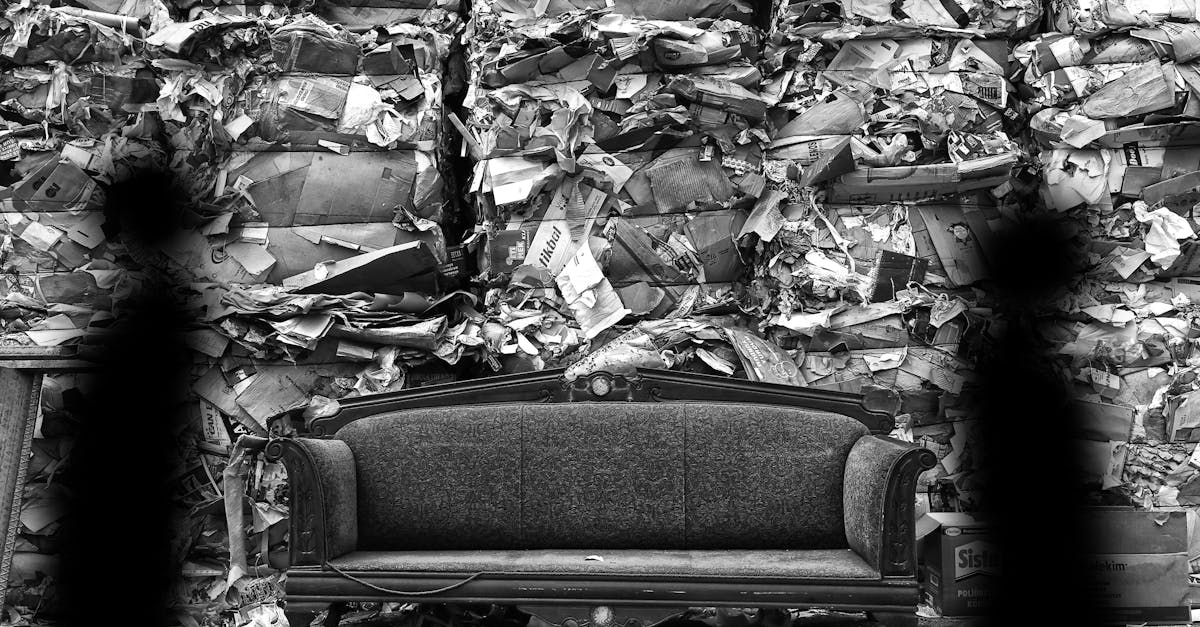

Business & Industrial
How Upcycling Old Paper Sparks Creative DIY Innovations
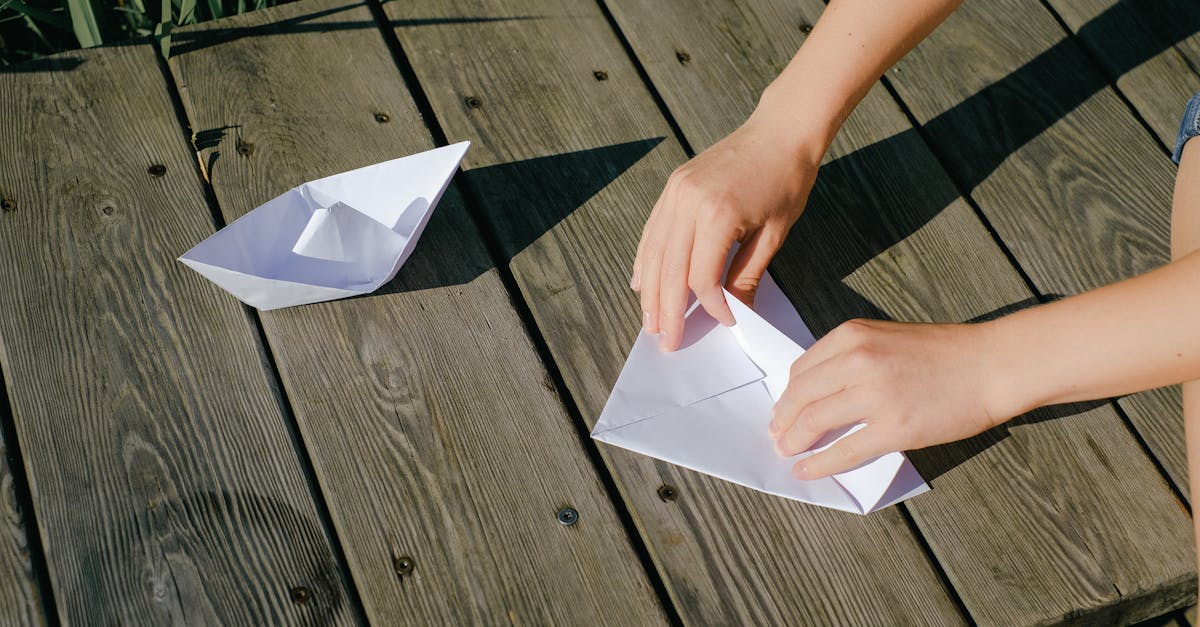
Hobbies & Leisure
Mastering Origami From Simple to Advanced Models
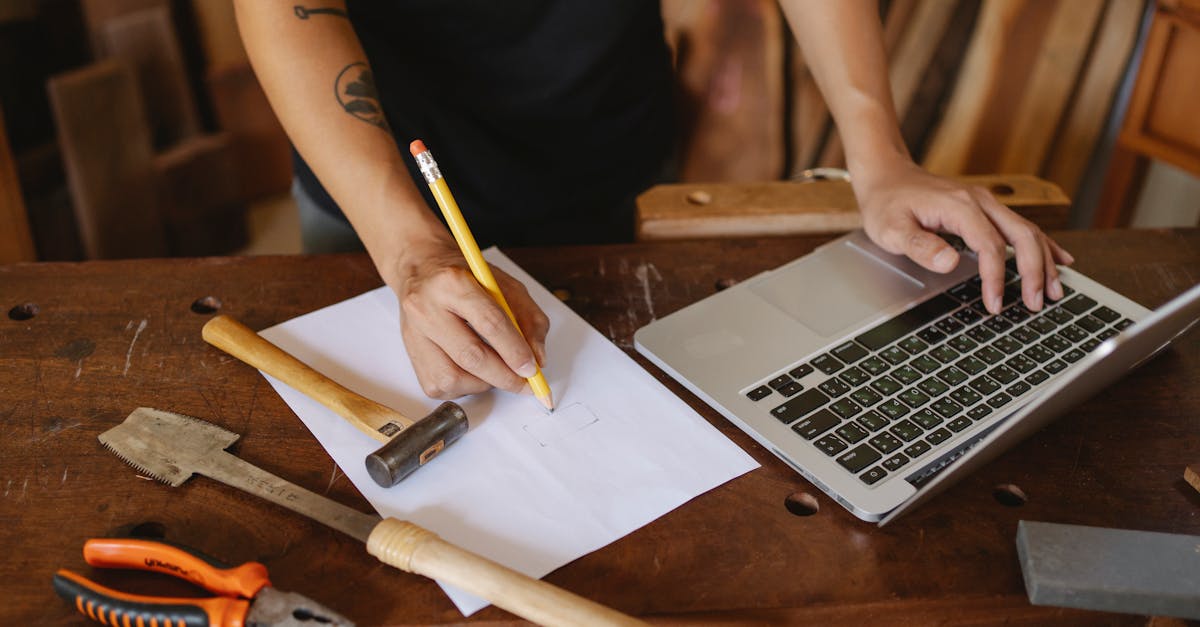

Blending Traditional Paper Crafts and Digital Design
Explore how paper crafts and digital designs can create stunning art through modern techniques and creativity.
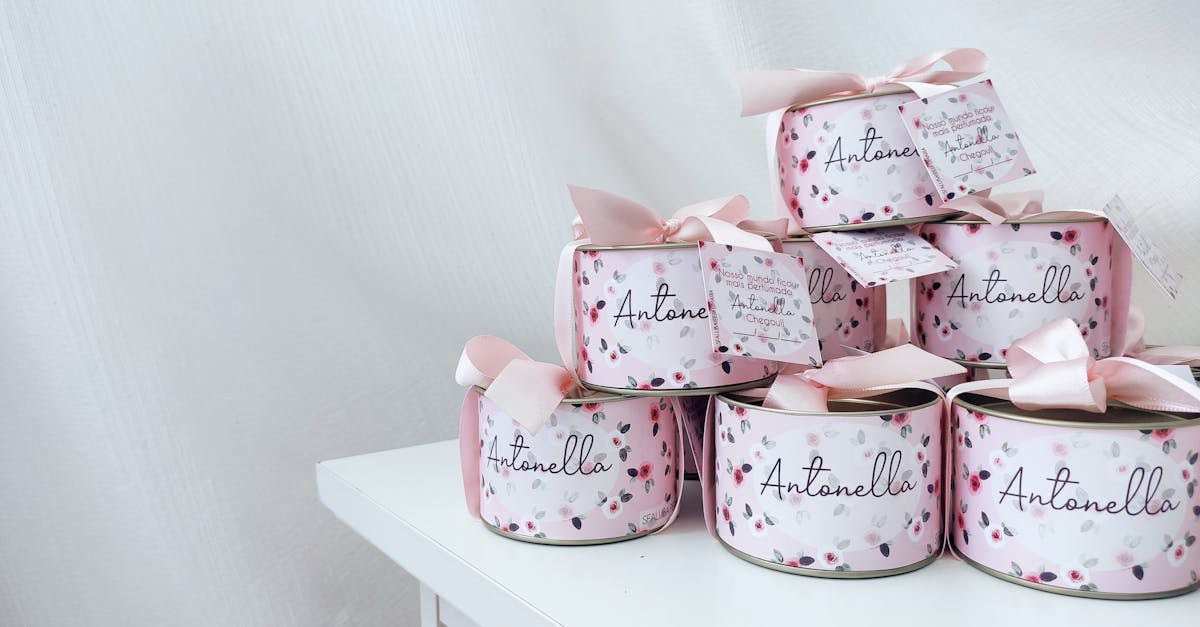

Personalized Paper Gifts Your Friends Will Love
Delight your friends with these creative and thoughtful personalized paper gifts for any occasion.
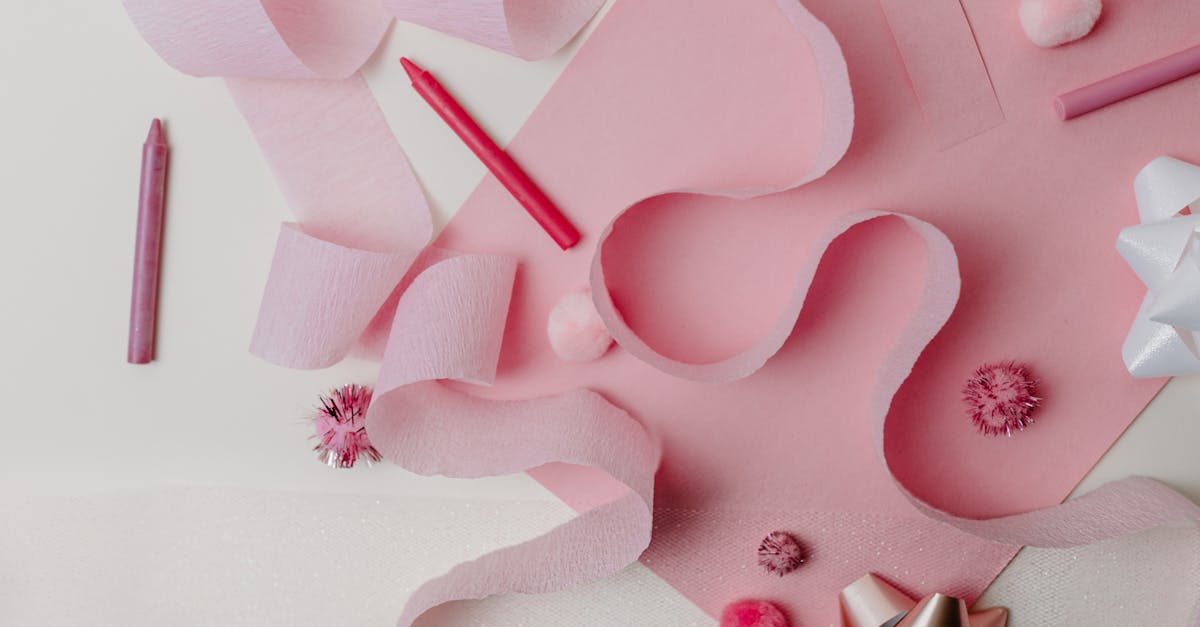

Budget Friendly Paper Crafts That Look Expensive
Discover how to create stunning paper crafts that give the appearance of luxury without breaking the bank.
